
You’ll find your business’s net income (or net loss) on the company’s most recent income statement. Note that, while in Step 2 you referred to last year’s balance sheet, for this portion of the exercise you’ll need the current year’s income statement. While you might need to refer to multiple financial documents, the process of calculating retained earnings is generally straightforward. Just be sure you have your company’s most recent balance sheet and income statement ready before you begin. If a company decides not to pay dividends, and instead keeps all of its profits for internal use, then the retained earnings balance increases by the full amount of net income, also called net profit.
- Retained earnings are reported in the shareholders‘ equity section of a balance sheet.
- Each period, the portion of net income kept by the company and not paid as dividends to shareholders flows into the retained earnings line item on the balance sheet (and increases its ending balance).
- Nevertheless, it’s important not to limit your fundamental stock research only to EPS, as other metrics should be evaluated as well to generate a well-rounded assessment.
- So, your company’s retained earnings for the third year are $300,000.
- Retained earnings represent the profits a business generates over time, while cash flow measures the net amount of cash/cash equivalents coming and and out over a given period of time.
- This money is reinvested to fuel growth, pay down debt, or strengthen operations.
- To start, you’ll need to know the retained earnings balance at the beginning of the period you’re calculating (typically the previous quarter or year).
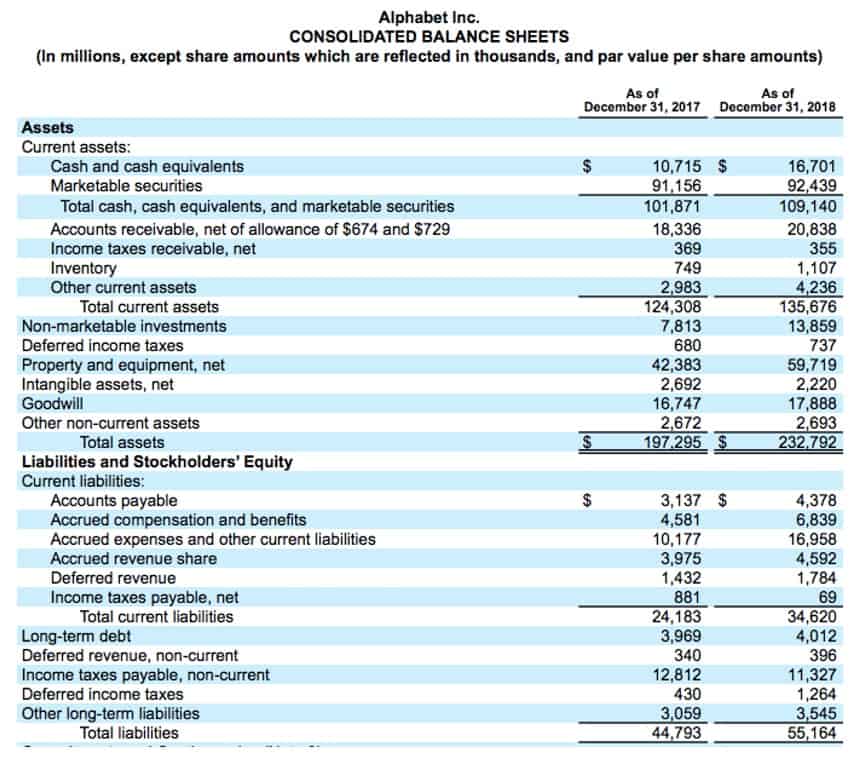
Classifying assets and liabilities
The amount transferred to the paid-in capital will depend upon whether the company has issued a small or a large stock dividend. Retained earnings at the beginning of the period are actually the previous year’s retained earnings. This can be found in the balance of the previous year, under the shareholder’s equity section on the liability side. In our example, December 2023 is the current year for which retained earnings need to be calculated, so December 2022 would be the previous year. Meaning the retained earnings balance as https://www.vijaytea.com/clarke-professional-accounting-2124-w-belmont-ave/ of December 31, 2022 would be the beginning period retained earnings for the year 2023. For example, if you prepare a yearly balance sheet, the current year’s opening balance of retained earnings would be the previous year’s closing balance of the retained earnings account.
Cash Dividend Example
If you’re calculating on an annual basis, for example, refer to the previous year’s balance sheet. Gross income refers to the business’ total revenues before deducting expenses, servicing debt, paying employees, and other mandatory payments. Net income is what’s left over after the business has met its obligations. These programs are designed to assist small businesses with creating financial statements, including retained earnings. It’s important to note that retained earnings are cumulative, meaning the ending retained earnings balance for one accounting period becomes the beginning retained earnings balance for the next period. When a company consistently experiences net losses, those losses deplete its retained earnings.
Share repurchases
Bench simplifies your small business accounting by combining intuitive software that automates the busywork with real, professional human support. This metric often reflects strategic reinvestment, especially for startups prioritizing market share, R&D, or product development. Net income accounts for all operating and non-operating expenses, while gross profit only subtracts direct cash flow production costs. Yes, retained earnings can be negative if a company has accumulated losses. The net change in NWC is $5 million, which reduces the company’s ending cash balance – i.e. the cash outflow offset and exceeded the cash inflow.
How Do You Prepare a Retained Earnings Statement?
In contrast, when a company suffers a net loss or pays dividends, the retained earnings account is debited, reducing the balance. Revenue, net profit, and retained earnings are terms frequently used on a company’s balance sheet, but it’s important to understand their differences. Well, to figure that out, take a peek at the shareholder’s equity section in your company’s balance sheet.
When lenders and investors evaluate a business, they often look beyond monthly net profit figures and focus on retained earnings. This is because retained earnings provide a more comprehensive overview of the company’s financial stability and long-term growth potential. A retail business might use retained earnings to open new stores without taking out loans. Another company could use them to pay off debt, lowering interest payments and improving cash flow. Retained earnings also help fund research and development, leading to new products or better services. The following is a simple example of calculating retained earnings based on the balance sheet and income statement information.
- It’s a simple way to track how well profits are being managed and reinvested.
- The culprit turned out to be retained earnings – the silent engine that funded their growth, cushioned their downturns, and decided their credibility to lenders.
- ’ The answer is no – it’s actually part of shareholders’ equity, representing accumulated earnings retained in the business.
- You can retain earnings, pay a cash dividend to shareholders, or choose a hybrid solution that addresses both.
- This doesn’t change the total size of the pie, just how many slices there are.
- For instance, say they look at your changes in retained earnings over the years.
Retained Earnings and Ending Cash Balance

Factors like sales revenue, expenses, and stocks play a big role in whether net income boosts or decreases retained earnings. For example, if you give one share as a dividend to each shareholder, it’s like cutting the pie into more slices – each slice gets smaller, but everyone still gets a piece. There are two types of dividends, cash or stock, and they affect your retained earnings.
Retained Earnings: Calculation, Formula & Examples
While the retention ratio looks at the percentage of net income you’re keeping, the dividend payout ratio looks at the percentage of net income you’re paying out to shareholders. If there were no dividends paid out, you don’t need to do any other adjustments from step two. Otherwise, subtract the full amount of dividends paid from the amount calculated in step two. It’s easy to understand the math if you think about what retained earnings actually are—the earnings that a company has kept (retained) over time instead of paying it out to shareholders. Learn how to build, read, and use financial statements for your business so you can make more informed decisions.
Brought to you by the company that works directly with the world’s top investment banks retained earnings formula and PE firms. The $10 million in depreciation expense reduces the PP&E balance, so the net PP&E balance in Year 0 is equal to $110 million. From Year 0 to Year 1, accounts receivable (A/R) increased by $10 million while accounts payable (A/P) increased by $5 million.
